Zero Vulnerability Computing (ZVC) for Open Source Connected Devices
Acronym: ZVC4IoT
Horizon Europe Call (21st October 2021): Topic ID: HORIZON-CL3-2021-CS-01-02
| # | Participant organization (acronym) | Type | Country | Expertise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P01 | University of Piraeus Research Center (UPRC) - Department of Informatics | UNI | EL | Project coordination, security architectures, malware analysis, threat analysis, applied crypto |
| P02 | Blockchain 5.0 O.Ü. (BC5) | SME | EE | Product development, cybersecurity-by-design, software architecture, decentralization |
| P03 | University of Thessaly (UTH) Department of Informatics and Telecommunications |
UNI | EL | Pervasive computing, Pervasive data science, Distributed Systems, Edge intelligence, IoT and ML/DL |
| P04 | Eurecat Technology Centre (EUT) | RES | ES | Medical Devices, IoT, Data and process management, AI |
| P05 | CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security | RES | DE | Cybersecurity and Cryptography |
| P06 | Zanasi Alessandro SRL ZAS | SME | IT | Cybersecurity, cyber risk assessment, ML and AI |
| P07 | Ethniko Kentro Erevnas Kai Technologikis Anaptyxis (CERTH) | RES | EL | AI-based cybersecurity, IoT middleware, Applications in e-Health, User acceptance and human factors in research |
| P08 | Autonio Foundation Ltd. (AFL) | NPO | UK | Artificial Intelligence, ML/DL, Decentralized AI, IPFS, P2P networking |
| P09 | SBA Research Gemeinnutzige GmbH (SBA) | RES | AT | Cybersecurity, Penetration Testing, Data privacy, Machine Learning (ML), ML Security & Privacy |
| P10 | Université de Lorraine (UL) Laboratoire Lorrain de Recherche en Informatique et ses Applications |
UNI | FR | Architectural and Algorithmic Solutions integrating ML Tools at the Edge, POD Management and Analytics, Intelligent Security Policy Enforcement |
Abstract
Cybercrime costs the global economy €5.6 Trillion annually. This is essentially because fool-proof cybersecurity of personal data in a connected computer is impossible. We are challenging that maxim and disrupting the status quo in cybersecurity with Zero Vulnerability Computing (ZVC). Two mandatory design attributes make computers usable, but also render them vulnerable. These necessary evils are:
- The permissions that computers grant to 3rd party applications, which bad actors and threat agent often abuse to create attack surface and vulnerabilities that attack vectors may exploit;
- The inherent vulnerability of data stored in-computer storage against an already compromised system.
In legacy computers neither the attack surface can be completely eliminated, nor can a connected device hold data offline, rendering fool-proof cybersecurity practically impossible. ZVC4IoT responds to the challenge of implementing zero vulnerability computing systems for specific environments, by designing, developing and integrating two radical paradigms:
- -Supra Operating System (SOS) a middleware software that obliterates the primary attack surface and,
- -In-Computer Offline Storage (ICOS) a hardware module that isolates critical data requiring sporadic access, in cold storage within the connected device itself.
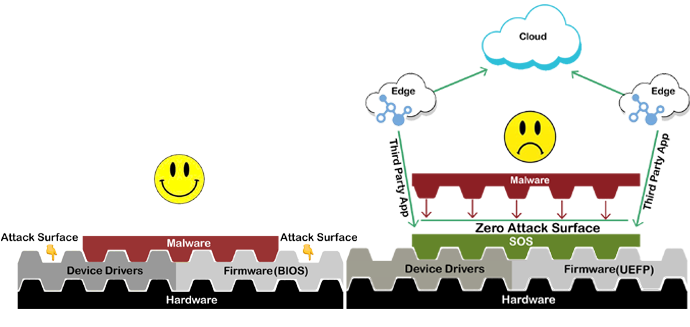

The combination of these two novel encryption-independant security paradigms, when properly designed in specific execution environments such as IoT devices, may lead to a computing environment with a very high cybersecurity assurance, against very strong and capable adversaries.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices became the most commonly attacked computing devices in 2019. With the IoT devices on the rise, this trend is exponentially growing. This is further worsened by the restricted environment of IoT devices that impose limitations on implementing complex security schemes making IoT security a real challenge. ZVC’s “Cybersecurity by Design” approach is based on a hypothesis that is currently under investigation at IMEC labs, Belgium, under H2020 grant. The main goal of ZVC4IoT is to establish the plausibility and efficacy of the ZVC framework in providing an end-user environment that will exhibit nearly zero exploitability for connected devices, particularly within the restricted Edge-IoT environment.
As proof of concept, we will design and implement ZVC in a typical Edge Network architecture, with 3 use cases that will evaluate characteristic scenarios involving pure IoT devices (such as smartwatches), hybrid devices (e.g. mobile phones) and high capability computing devices (laptop, PC) as edge devices. The implementation of this ambitious goal will be supported through a well defined and complementary consortium with strong background in cybersecurity that involves 6 participants from the 4 EU-funded pilot projects (CyberSec4Europe, CONCORDIA, SPARTA & ECHO) for developing Cybersecurity Competence Network along with other participants with strong background cybersecurity, cryptography, hardware, machine learning and dissemination / exploitation background.